Bug Fixes:
Resin – 4.0.59 – in progress
==============
- 0006180: Double quotes not set through web server
- 0006181: SSL protocol update in Quercus
- 0006177: Deadlock starting ResinEmbed
- 0006184: Path-based XSS in redirects from FileServlet
Resin – 4.0.58 – currently available
==============
- 0006170: ByteCodeClassScanner fails for packages with JDK9 module-info.class files
- 0006168: AsyncServlet Wake-up occasionally looses events
- 0006171: <load-on-startup> retry logic customization
- 0006169: Enable/Disable Openssl protocols from resin.properties
- 0006166: All threads associated with a port disappear
- 0006172: request parameters not kept immutable – 0006167: cookie-same-site
Release Schedule
Resin 4 releases are scheduled every 5-7 weeks. With releases including performance enhancements, bug fixes, feature requests, and security patches it is advisable to be running the most current version of Resin in production.
For details or questions about specific fixes & vulnerabilities that have been patches in releases, email wiley@caucho.com
JDK Updates
Java development has a new release cadaence with releases coming every 6 months. The new release schedule calls for a feature release every six months, update releases every quarter, and a long-term support (LTS) release every three years.
The current release schedule is as follows:
Resin 4.0.57+ currently supports JDK 9 and can be downloaded on the Caucho website. Future releases of the JDK will be fully supported by Resin weeks after initial Java releases are made public.
If you need to start development with a new version of Java before our official Resin release, feel free to ask us about an early snapshot!
Embedded Resin
An embeddable version of the Resin server can be useful in instances where a user would like to package both the app & app server together, reducing potential complexities for deployment. With deployment orchestration and container platforms like Kubernetes & Docker gaining usage, embedding Resin can aid in creating deployable runtime environments.
Q: Are there any performance implications running Resin in this fashion?
Nope! The *Embed objects are only used to configure the regular Resin server. Once the server is configured they become discarded or unused.
The main Resin embed class is com.caucho.resin.ResinEmbed. Additionally, the http://javadoc4.caucho.com/ website provides documentation on embedding Resin.
The main Resin class: com.caucho.server.resin.Resin, can be bootstrapped for additional capabilities.
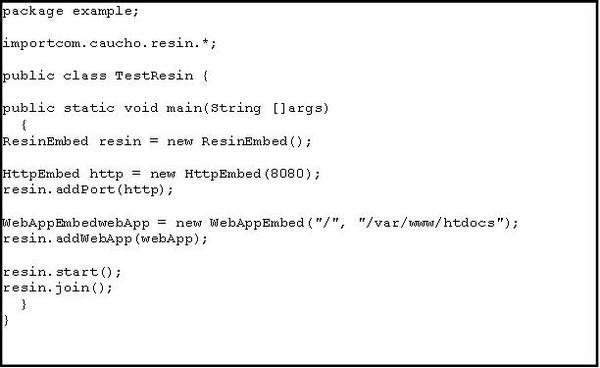
For a simple application, com.caucho.resin.ResinEmbed, HttpEmbed (for port) and WebAppEmbed are the classes you need first. An example is provided below:
How are you using Resin?
 We'd like to hear from you!!
We'd like to hear from you!!
Our quarterly newsletter reaches 8700 readers.
If you have an application that deserves the
spotlight, email Alexandra at garmon@caucho.com
to share your story. We can create a case study
or even a fun paragraph with a link to show off your work.
(Caucho CEO, Steve Montal @ Comic Con 2018)
Resin Cookbooks
Simple 10-minute overviews of various Resin topics are available on the Caucho website. For new users or even users who want brief refreshers on advanced Resin topics, the cookbooks are a great place to start.
Resin Deployment
–basic application deployment on Resin
Resin Debugging
–useful debugging tools for Resin deployments
Resin on Amazon EC2
–get setup on Amazon EC2 in minutes
Resin Security
– 4 ways to secure your deployment
Resin Checksum
For verifying your Resin download, the following url format and location can be used to view the sha256 checksum:

Example:
https://caucho.com/download/resin-pro-4.0.55.tar.gz.sha256